IPSec VPN
IPSec facilitates configuration of secured communication tunnels. The various tunnel configurations will be displayed in the Tunnel Table at the bottom of the page. All tunnels are create using the ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) protocol.

Status
|
Field |
Description |
|
Displays current IPSec settings is enable or disable. |
|
Displays the description of current VPN channel. |
|
Displays the current VPN connection status. |
|
Displays the connection time since VPN is established. |
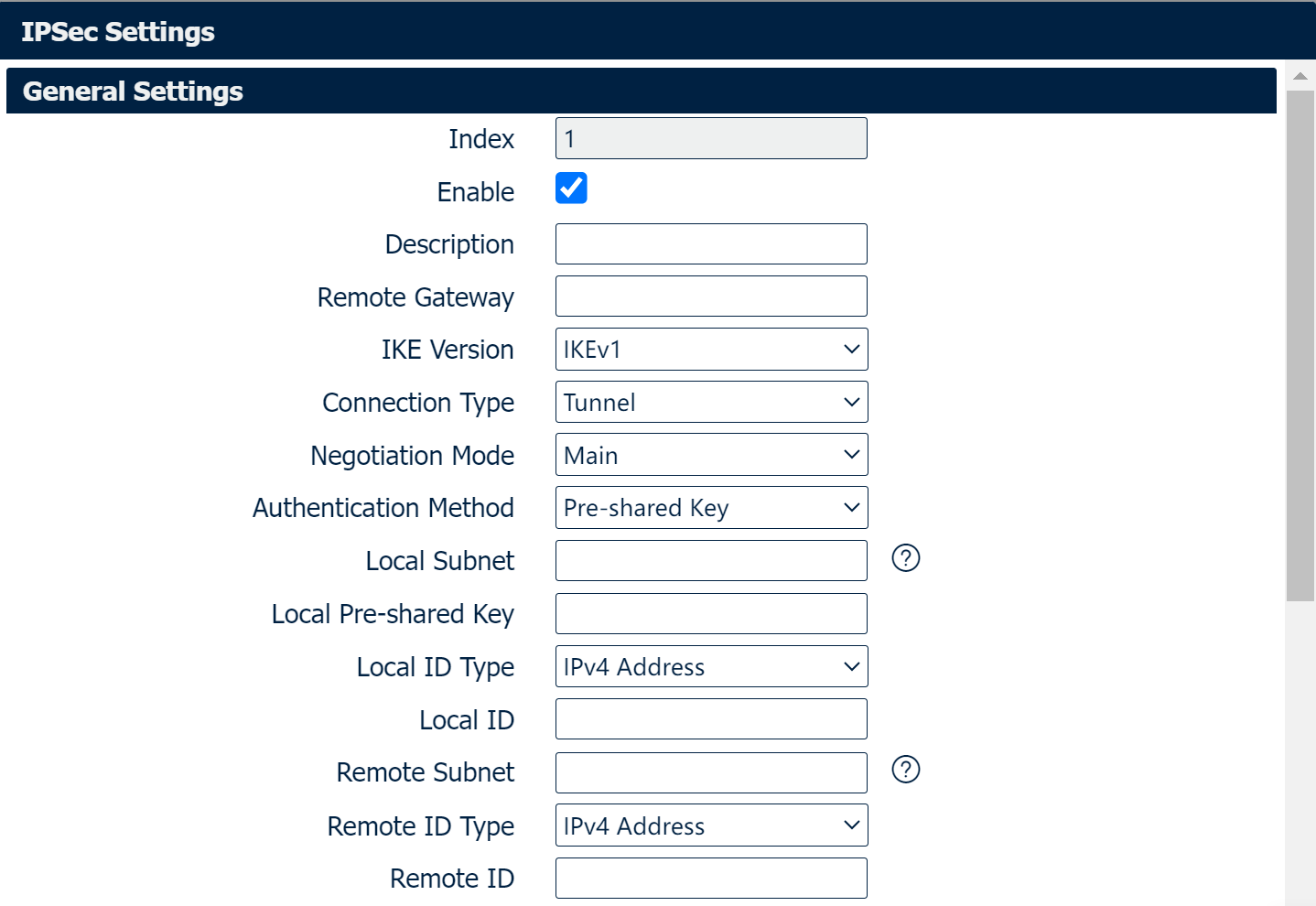
General Settings
|
Field |
Description |
|
Select Enable will launch the IPSec process. |
|
Enter a description for this IPSec VPN tunnel. |
|
Enter the IP address of the remote endpoint of the tunnel. |
|
Internet Key Exchange, select from “IKEv1” or “IKEv2”. |
|
Select from “Tunnel” or “Transport”. Transport: In transport mode, only the payload of the IP packet is usually encrypted or authenticated. The routing is intact, since the IP header is neither modified nor encrypted. |
|
Select from “Main” or “Aggressive”. |
|
Select from “Pre-shared Key” or “Pre-shared Key and Xauth”. |
|
Ener the IP address with mask if a network beyond the local LAN will be sending packets through the tunnel. Multiple subnets separated by commas. NOTE: The Remote subnet and Local subnet addresses must not overlap! |
|
Enter the pre-shared key which match the remote endpoint. |
|
Select from “IPv4 Address”, “FQDN”, “User-FQDN” for authentication with the remote endpoint. |
|
The content of Local ID need to match “Local ID type”. |
|
Enter Xauth identity after “Pre-shared Key and Xauth” on authentication Method is enabled. |
|
Enter Xauth password “Pre-shared Key and Xauth” on authentication Method is enabled. |
|
Enter an IP address with mask if encrypted packets are also destined for the specified network that is beyond the Remote IP Address. Multiple subnets separated by commas. NOTE: The Remote subnet and Local subnet addresses must not overlap! |
|
Select from “IPv4 Address”, “FQDN”, “User-FQDN” for authentication with the remote endpoint. |
|
The content of Remote ID need to match “Remote ID type”. |
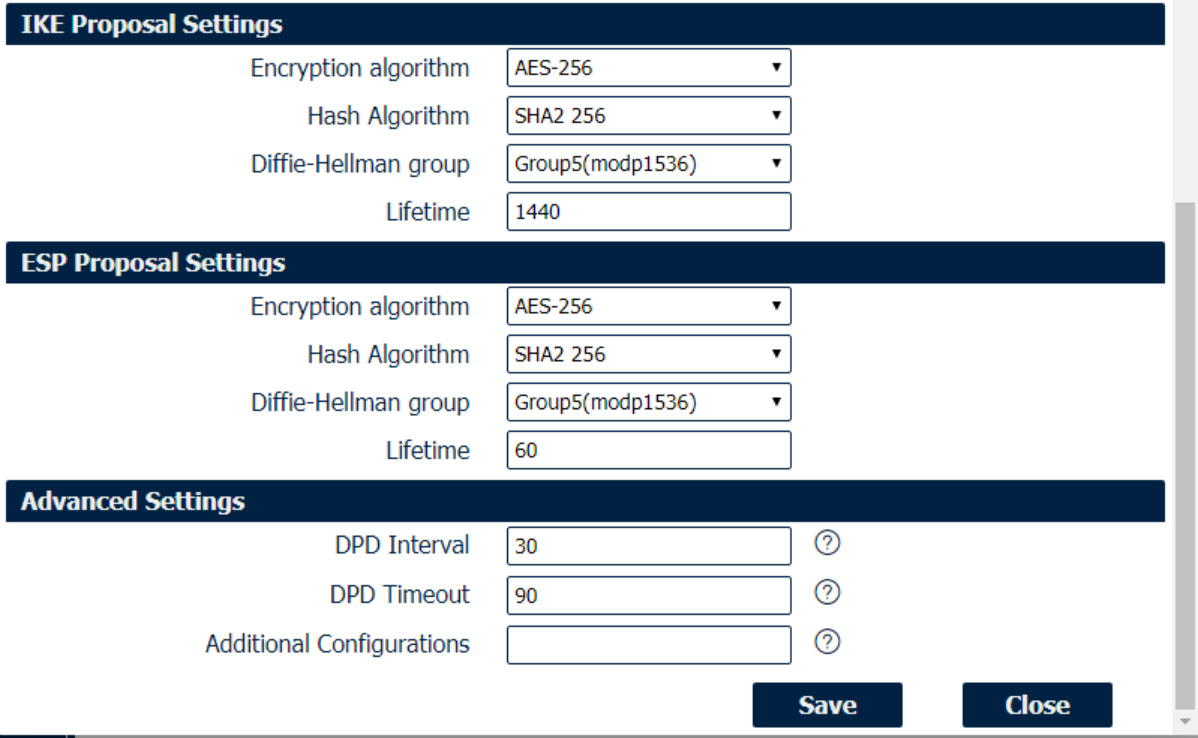
IKE/ESP/Advanced Settings
|
Field |
Description |
|
Select 3DES AES-128, AES-192, or AES-256 encryption. |
|
Select from MD5, SHA1, SHA2 256, SHA2 384 or SHA2 512 hashing. |
|
Negotiate (None) or use 768 (Group 1), 1024 (Group 2), 1536 (Group 5) or 2048 (Group 14) etc. |
|
How long the keying channel of a connection should last before being renegotiated. |
|
Select 3DES AES-128, AES-192, or AES-256 encryption. |
|
Select from MD5, SHA1, SHA2 256, SHA2 384 or SHA2 512 hashing. |
|
Negotiate (None) or use 768 (Group 1), 1024 (Group 2), 1536 (Group 5) or 2048 (Group 14) etc. |
|
How long a particular instance of a connection should last, from successful negotiation to expiry. |
|
Enter the interval after which DPD is triggered if no IPsec protected packets is received from the peer. |
|
Enter the remote peer probe response timer. |
|
Enter some other options of IPSec in this field. Each expression can be separated by a ‘;’. |